ग्वालियर किला / Gwalior Fort
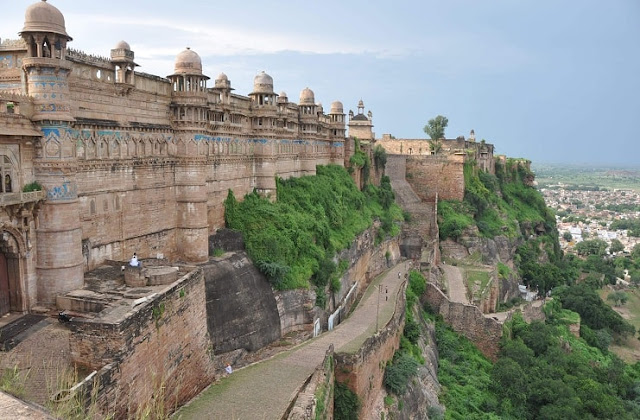
ग्वालियर किला ग्वालियर, मध्य प्रदेश, मध्य भारत के पास स्थित एक पहाड़ी किला है। किले का अस्तित्व कम से कम 10 वीं शताब्दी के पहले से है, और अब जो किला परिसर है, उसके भीतर मिले शिलालेखों और स्मारकों से पता चलता है कि यह 6 वीं शताब्दी की शुरुआत में मौजूद था। ग्वालियर किला अपने इतिहास में कई अलग-अलग शासकों द्वारा नियंत्रित किया गया है।
 |
| Gwalior Fort |
ग्वालियर किला की स्थापत्य शैली
ग्वालियर किला के परिसर में अनेकों महल, मंदिर और पानी के टैंक सहित कई ऐतिहासिक स्मारक हैं। मान मंदिर, गुजरी, जहाँगीर, करण और शाहजहाँ सहित कई महल भी हैं। किला 3 वर्ग किलोमीटर (1.2 वर्ग मील) के क्षेत्र को कवर करता है और 11 मीटर (36 फीट) बढ़ जाता है। इसका प्राचीर पहाड़ी के किनारे पर बना है, जो छह गढ़ों या मीनारों से जुड़ा है।
किले के दो द्वार हैं; उत्तर-पूर्व की ओर एक लंबी पहुंच वाली रैंप और दूसरी दक्षिण-पश्चिम की ओर। मुख्य द्वार अलंकृत हाथी द्वार (हाथी पुल) है। दूसरा बादलगढ़ गेट है। मैन मंदिर महल या गढ़ किले के पूर्वोत्तर छोर पर स्थित है। यह 15 वीं शताब्दी में बनाया गया था और 1648 में इसे नवीनीकृत किया गया था। किले के पानी के टैंक या जलाशय 15,000 मजबूत घाटियों को पानी प्रदान कर सकते हैं।
इतिहास / History of Gwalior Fort
ग्वालियर किला के निर्माण की सही अवधि निश्चित नहीं है। एक स्थानीय किंवदंती के अनुसार, किले का निर्माण 3 इस्वी में सूरज सेन नाम के एक स्थानीय राजा ने करवाया था। वह कुष्ठ रोग से ठीक हो गया, जब ग्वालिप्पा नामक एक ऋषि ने उसे पवित्र तालाब से पानी देने की पेशकश की, जो अब किले के भीतर स्थित है। कृतज्ञ राजा ने एक किले का निर्माण किया, और इसका नाम ऋषि के नाम पर रखा। ऋषि ने राजा पर पाल ("रक्षक") की उपाधि दी, और उसे बताया कि जब तक वे इस उपाधि को धारण करेंगे, तब तक ग्वालियर किला उनके परिवार के कब्जे में रहेगा। सूरज सेन पाल के 83 वंशजों ने किले को नियंत्रित किया, लेकिन 84 वें तीज करण नाम ने इसे खो दिया।
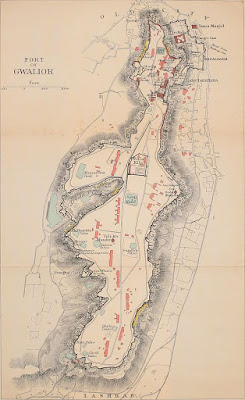 |
| Gwalior Fort Map |
अब जो किला परिसर है उसके भीतर मिले शिलालेख और स्मारक संकेत करते हैं कि यह 6 वीं शताब्दी की शुरुआत में मौजूद था। ग्वालियर किला के एक शिलालेख में 6 वीं शताब्दी में हुना सम्राट मिहिरकुला के शासनकाल के दौरान निर्मित एक सूर्य मंदिर का वर्णन है। तेली का मंदिर, जो अब किले के भीतर स्थित है, 9 वीं शताब्दी में गुर्जर-प्रतिहारों द्वारा बनाया गया था। दसवीं शताब्दी तक निश्चित रूप से किले का अस्तित्व था, जब पहली बार ऐतिहासिक अभिलेखों में इसका उल्लेख किया गया था। कच्छपघाट ने इस समय किले को नियंत्रित किया, जो शायद चंदेलों के सामंतों के रूप में था। 11 वीं शताब्दी से, मुस्लिम राजवंशों ने कई बार किले पर हमला किया। घुरिद के जनरल कुतुब अल-दीन ऐबक, जो बाद में दिल्ली सल्तनत के शासक बना, उस ने 1196 में लंबी घेराबंदी के बाद किले पर कब्जा कर लिया। 1232 ईसा में इल्तुमिश द्वारा हटाए जाने से पहले दिल्ली सल्तनत ने थोड़े समय के लिए किले को खो दिया।
1398 में, ग्वालियर किला तोमरों के नियंत्रण में आ गया। तोमर शासकों में सबसे प्रतिष्ठित मान सिंह थे, जिन्होंने किले के भीतर कई स्मारकों को चालू किया था। दिल्ली सुल्तान सिकंदर लोदी ने 1505 में किले पर कब्जा करने की कोशिश की, लेकिन असफल रहा। 1516 में उनके बेटे इब्राहिम लोदी द्वारा एक और हमला किया गया, जिसमें मान सिंह जी की मृत्यु हुई। परिणामस्वरूप तोमरों ने अंततः एक साल की घेराबंदी के बाद किले को दिल्ली सल्तनत को सौंप दिया। अकबर के समय में किले को राजनीतिक कैदियों के लिए जेल बना दिया। उदाहरण के लिए, कामरान और अकबर के पहले चचेरे भाई के बेटे अबुल-कासिम को किले में रखा गया और मार डाला गया। 1609 में मुगल बादशाह जहांगीर ने सिखों के छठे गुरु हरगोविंद सिंह जी को 14 वर्ष की आयु में बंदी बना कर इसी किले में रखा था।
18 वीं शताब्दी में मराठा जनरल महादाजी शिंदे (सिंधिया) ने गोहद राणा छतर सिंह से ग्वालियर किला पर कब्जा कर लिया, लेकिन जल्द ही इसे ब्रिटिश ईस्ट इंडिया कंपनी से हार गए। 1808 और 1844 के बीच सिंधिया और अंग्रेजों के बीच किले के नियंत्रण में लगातार बदलाव हुए। जनवरी 1844 में, महाराजपुर की लड़ाई के बाद, मराठा सिंधिया परिवार ने अंग्रेजों के रक्षक के रूप में ग्वालियर राज्य पर कब्जा कर लिया। 1857 के विद्रोह के दौरान, ग्वालियर में तैनात लगभग ६५०० सिपाहियों ने कंपनी शासन के खिलाफ विद्रोह किया, हालाँकि कंपनी के जागीरदार शासक जयाजी सिंधिया अंग्रेजों के प्रति वफादार रहें। सिंधिया घराणेने भारत की स्वतंत्रता तक ग्वालियर पर शासन करते रहे, और जय विलास महल सहित कई स्मारकों का निर्माण किया।
अन्य तथ्य
वर्तमान किले में एक रक्षात्मक संरचना और दो मुख्य महल, गुजरी महल और मान मंदिर, जो कि मान सिंह तोमर द्वारा निर्मित (1416-1516 CE) हैं। गुजरी महल रानी मृगनयनी के लिए बनाया गया था। यह अब एक पुरातात्विक संग्रहालय है।
दुनिया में "शून्य (zero)" का दूसरा सबसे पुराना रिकॉर्ड एक छोटे से मंदिर में पाया गया था, जो शीर्ष पर स्थित है। यह शिलालेख लगभग 1500 साल पुराना है।
 |
| Gwalior Fort |
पर्यटन के लिए आवश्यक जानकारियां / when to visit Gwalior Fort
- किला खुलने का समय: सुबह 6:00 बजे
- समापन समय: शाम 5:30 बजे
- प्रवेश शुल्क: 75 ₹ प्रति व्यक्ति
- विदेशी नागरिक: 250 प्रति ₹ व्यक्ति
- बच्चे (15 वर्ष से कम): नि: शुल्क
------------------------------------------------
English Version
ग्वालियर किला / Gwalior Fort
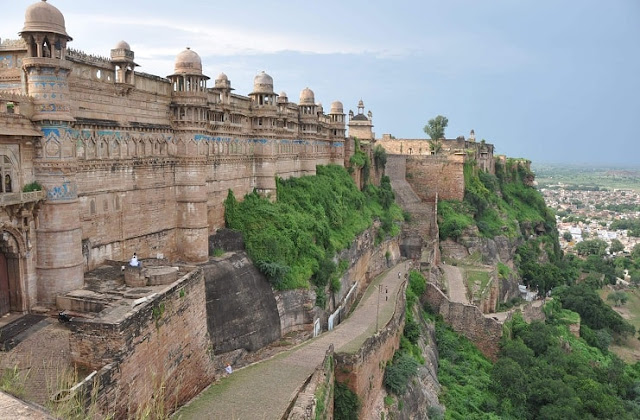
Gwalior Fort is a hill fort located near Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh, Central India. The fort has existed since at least the 10th century, and the inscriptions and monuments found within the fort complex that now exists suggest that it existed in the early 6th century. The fort has been controlled by many different rulers throughout its history.
 |
| ग्वालियर किला / Gwalior fort |
Architectural style of Gwalior Fort
The complex of the Gwalior Fort has many historical monuments including many palaces, temples and water tanks. There are many palaces including Maan Mandir, Gujri, Jahangir, Karan and Shah Jahan. The fort covers an area of 3 square kilometers (1.2 sq mi) and rises 11 meters (36 ft). Its ramparts are built on the side of the hill, connected by six bastions or minarets.
The Gwalior Fort has two gates; One long access ramp to the northeast and the other to the southwest. The main gate is the ornate elephant gate (elephant bridge). The second is Badalgarh Gate. The Man Mandir is located at the northeast end of the palace or the citadel. It was built in the 15th century and was renovated in 1648. The fort's water tanks or reservoirs can provide water to 15,000 strong valleys.
इतिहास / History of Gwalior Fort
The exact period of construction of Gwalior Fort is not certain. According to a local legend, the fort was built in 3 AD by a local king named Suraj Sen. He was cured of leprosy, when a sage named Gwalippa offered him water from the sacred pond, which is now located within the fort. The grateful king built a fort, and named it after the sage. The sage conferred the title of Pal ("protector") on the king, and told him that the fort would remain in the possession of his family as long as they would hold this title. 83 descendants of Suraj Sen Pal controlled the fort, but the 84th Teej Karan Naam lost it.
 |
| ग्वालियर किला / Gwalior fort |
Inscriptions and monuments found inside the fort complex now indicate that it existed in the early 6th century. An inscription from Gwalior describes a Sun Temple built in the 6th century during the reign of Huna Emperor Mihirkula. The Teli temple, now located within the fort, was built by Gurjara-Pratiharas in the 9th century. The fort certainly existed until the tenth century, when it was first mentioned in historical records. Kachhapaghat controlled the fort at this time, probably as the feudatories of the Chandelas. From the 11th century, Muslim dynasties attacked the fort several times. Qurub al-Din Aibak, the general of Ghurid, who later became the ruler of the Delhi Sultanate, captured the fort in 1196 after a long siege. The Delhi Sultanate lost the fort for a short time before being removed by Iltumish in 1232 AD.
In 1398, the Gwalior Fort came under the control of the Tomars. The most eminent of the Tomar rulers was Man Singh, who commissioned several monuments within the fort. Delhi Sultan Alexander Lodi tried to capture the fort in 1505, but was unsuccessful. In 1516, there was another attack by his son Ibrahim Lodi, in which Man Singh ji died. As a result, the Tomars finally handed over the fort to the Delhi Sultanate after a year of siege. In Akbar's time, the fort was made a prison for political prisoners. For example, Abul-Qasim, son of Kamran and Akbar's first cousin, was placed in the fort and killed. In 1609, the Mughal emperor Jahangir had arrested the sixth Sikh Guru Hargovind Singh Ji at the age of 14 and kept him in this fort.
In the 18th century, the Maratha general Mahadaji Shinde (Scindia) captured the Gwalior Fort from Gohad Rana Chhatar Singh, but soon lost it to the British East India Company. Between 1808 and 1844, there were frequent changes in the control of the fort between Scindia and the British. In January 1844, after the Battle of Maharajpur, the Maratha Scindia family captured the state of Gwalior as a protector of the British. During the Revolt of 1857, about 8500 soldiers stationed in Gwalior revolted against the company rule, although the company's vassal ruler Jayaji Scindia remained loyal to the British. Scindia Gharane continued to rule Gwalior till the independence of India, and built many monuments including the Jai Vilas Palace.
Other Facts about Gwalior Fort
The present Gwalior Fort has a defensive structure and two main palaces, the Gujari Mahal and the Maan Temple, built by Man Singh Tomar (1416–1516 CE). Gujari Mahal was built for Queen Mriganayani. It is now an archaeological museum.
The second oldest record of "zero" in the world was found in a small temple, which is located at the top. This inscription is about 1500 years old.
 |
| ग्वालियर किला / Gwalior fort |





No comments:
Post a Comment